Architectural Styles
An Architectural Style is characterized by the features that make a building or other structure notable and historically identifiable. A Style may include such elements as form, method of construction, building materials, and regional character. Most architecture can be classified as a chronology of Styles which change over time reflecting changing Fashions, Beliefs and Religions, or the emergence of new ideas, technology, or materials which make new Styles possible.
Louis XIII
The Louis XIII style was a fashion in French Art and Architecture, especially affecting the visual and decorative arts. Its distinctness as a period in the history of Louis XIII.
Louis XIV
The Louis XIV Style, also called French Classicism, was the style of architecture and decorative arts intended to glorify King Louis XIV and his reign. It featured majesty, harmony, and regularity. It became the official style during the reign of Louis XIV.
Louis XV
The Louis XV style is a style of architecture and decorative arts which appeared during the reign of Louis XV of France, it was largely an extension of the "Style Louis XIV" of his great-grandfather and predecessor, Louis XIV of France. It became more original, decorative and exuberant, in what was known as the rocaille style, under the influence of the King's mistress, Madame de Pompadour. It marked the beginning of the European Rococo movement.
Louis XVI
Louis XVI style is a Style of Architecture, Furniture, Decoration and Art which developed in France during the 19-year reign of Louis XVI, just before the French Revolution. It was inspired in part by the discoveries of ancient Roman paintings, sculpture and architecture in Herculaneum and Pompeii. Its features included the straight column, the simplicity of the post-and-lintel, the architrave of the Greek temple.
Empire
The Empire style is an early-nineteenth-century design movement in Architecture, Furniture, other Decorative Arts, and the Visual Arts, representing the second phase of Neoclassicism. The Style originated in and takes its name from the rule of the Emperor Napoleon I in the First French Empire, when it was intended to idealize Napoleon's leadership and the French State.
Louis XVIII
The Style of Architecture and Design under King Louis XVIII was a more eclectic development of French Neoclassicism, incorporating elements of Neo-Gothic and other Styles. It was the first French Decorative Style imposed not by Royalty, but by the tastes of the growing French upper class. In painting, neoclassicism and romanticism contended to became the dominant style.
Napoléon III
The Napoleon III Style was a highly Eclectic Style of Architecture and Decorative Arts, which used elements of many different historical Styles and also made innovative use of modern materials, such as Iron Frameworks and Glass Skylights. It flourished during the reign of Emperor Napoleon III in France and had an important influence on Architecture and Decoration in the rest of Europe and the United States. The Architectural Style was closely connected with Haussmann's renovation of Paris carried out during the Second Empire.
Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau is an International Style of Art, Architecture and applied Art, especially the Decorative Arts. It was most popular between 1890 and 1910. A reaction to the Academic Art of the 19th century, it was inspired by natural forms and structures, particularly the curved lines of plants and flowers.
Art Nouveau is a comprehensive Art Style that encompasses a wide range of Fine and Decorative Arts, including Architecture, Painting, Graphic Art, Interior Design, Jewelry, Furniture, and Metalwork.
Art Déco
Art Déco, is a Style of Architecture and Design that first appeared in France just before World War I. Art Déco influenced the Design of Buildings, Furniture, Jewelry, Fashion, and everyday objects. It took its name, short for Arts Décoratifs, from the International Exhibition of Modern Decorative and Industrial Arts held in Paris in 1925. It combined Modern Styles with Fine Craftsmanship and Rich Materials. During its heyday, Art Déco represented Luxury, Glamour, Exuberance, and faith in social and technological progress.
Art Contemporain
Art Contemporain is the Art of Today, produced in the second half of the 20th century or in the 21st century. Contemporary Artists work in a globally influenced, culturally diverse, and technologically advancing world. Their Art is a dynamic combination of materials, methods, concepts, and subjects that continue the challenging of boundaries that was already well underway in the 20th century. Diverse and eclectic, Art Contemporain as a whole is distinguished by the very lack of a uniform, organising principle, and ideology.
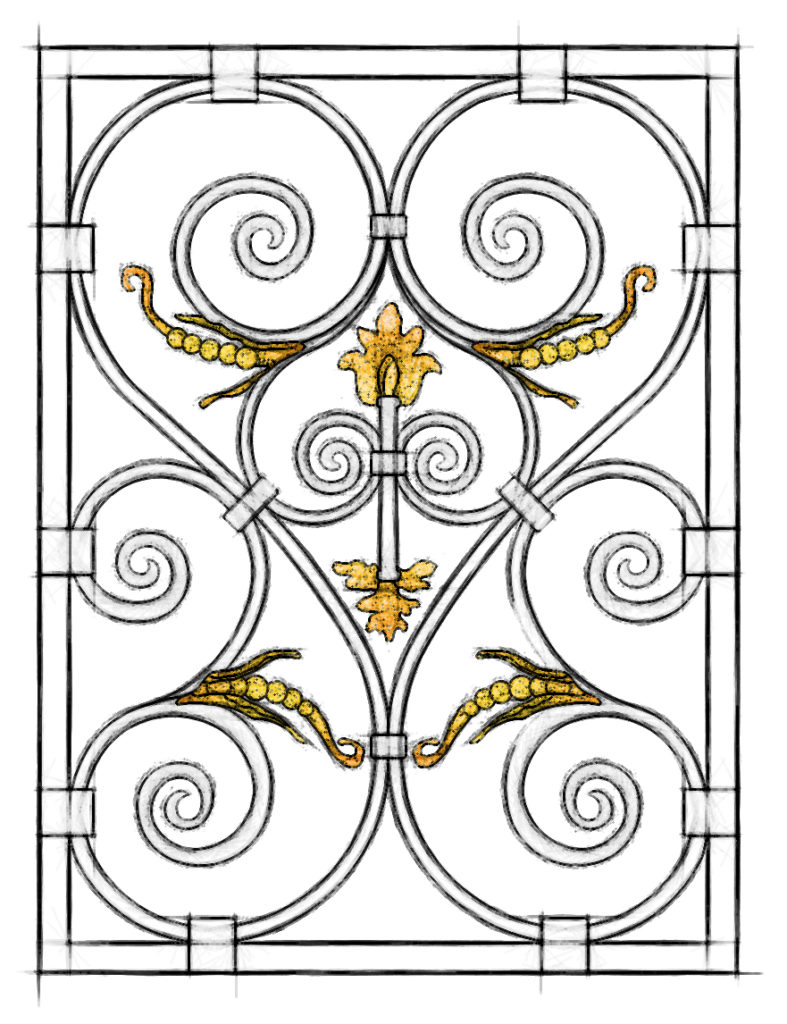
The Louis 13 style was a fashion in French Art and Architecture, especially affecting the visual and decorative arts. Its distinctness as a period in the history of French art has much to do with the regency under which Louis 13.
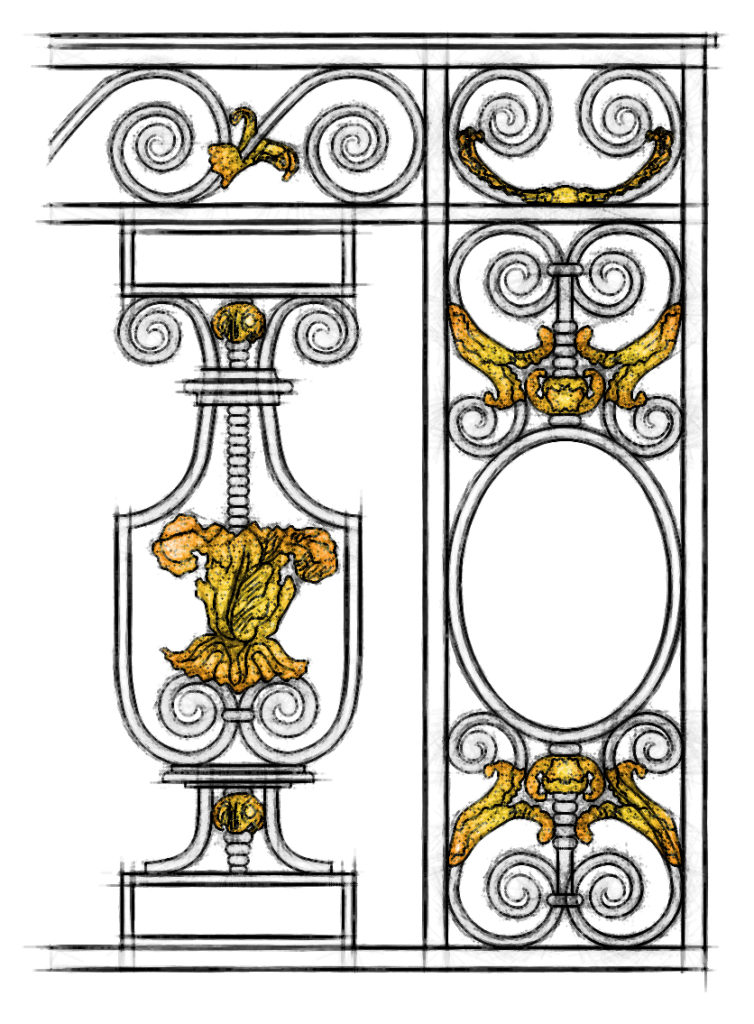
The Style Louis 14, also called French classicism, was the style of architecture and decorative arts intended to glorify King Louis 14 and his reign. It featured majesty, harmony and regularity. It became the official style during the reign of Louis 14.
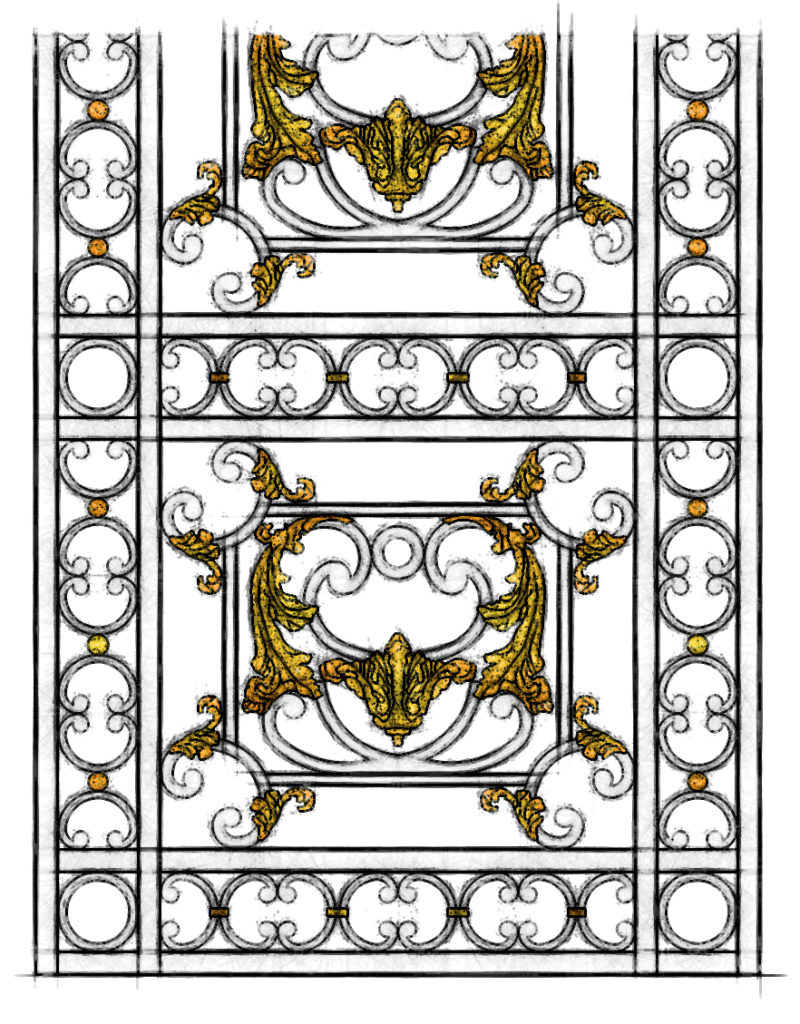
The Louis 15 style is a style of architecture and decorative arts which appeared during the reign of Louis 15 of France, it was largely an extension of the « Style Louis 14 » of his great-grandfather and predecessor, Louis 14 of France. It became more original, decorative and exuberant, in what was known as the rocaille style, under the influence of the King’s mistress, Madame de Pompadour. It marked the beginning of the European Rococo movement.
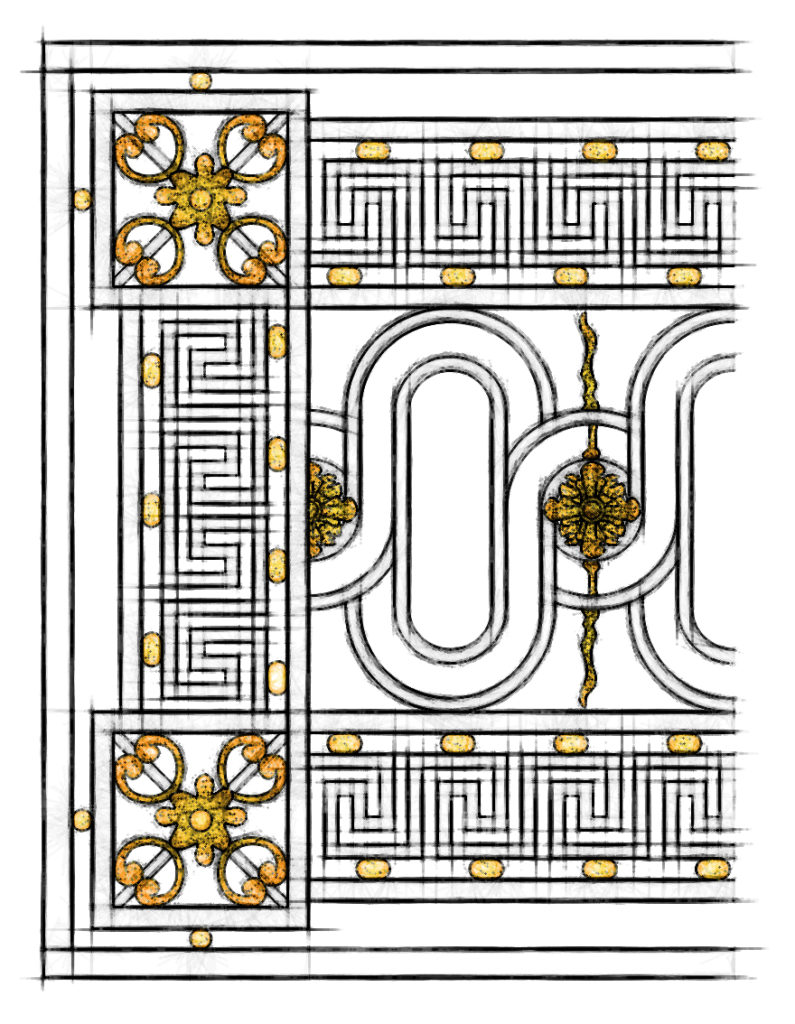
Louis 16 style is a style of architecture, furniture, decoration and art which developed in France during the 19-year reign of Louis 16, just before the French Revolution. It was inspired in part by the discoveries of ancient Roman paintings, sculpture and architecture in Herculaneum and Pompeii. Its features included the straight column, the simplicity of the post-and-lintel, the architrave of the Greek temple.
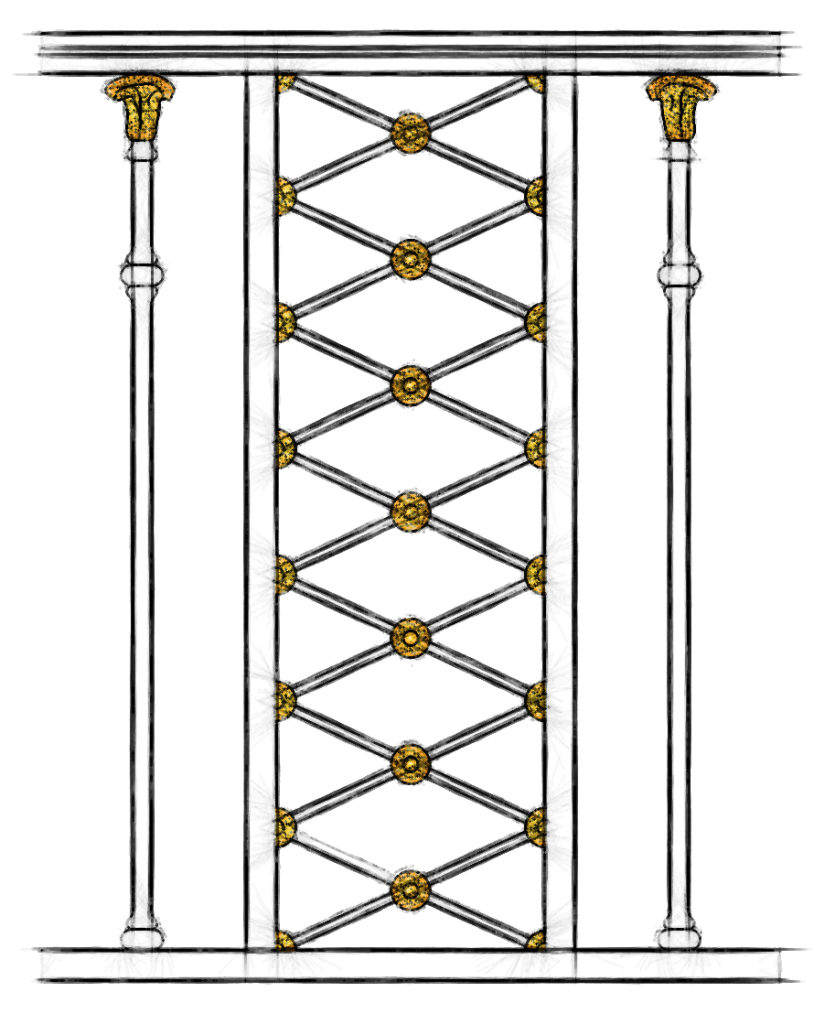
The Empire style is an early-nineteenth-century design movement in architecture, furniture, other decorative arts, and the visual arts, representing the second phase of Neoclassicism. The style originated in and takes its name from the rule of the Emperor Napoleon I in the First French Empire, when it was intended to idealize Napoleon’s leadership and the French state.
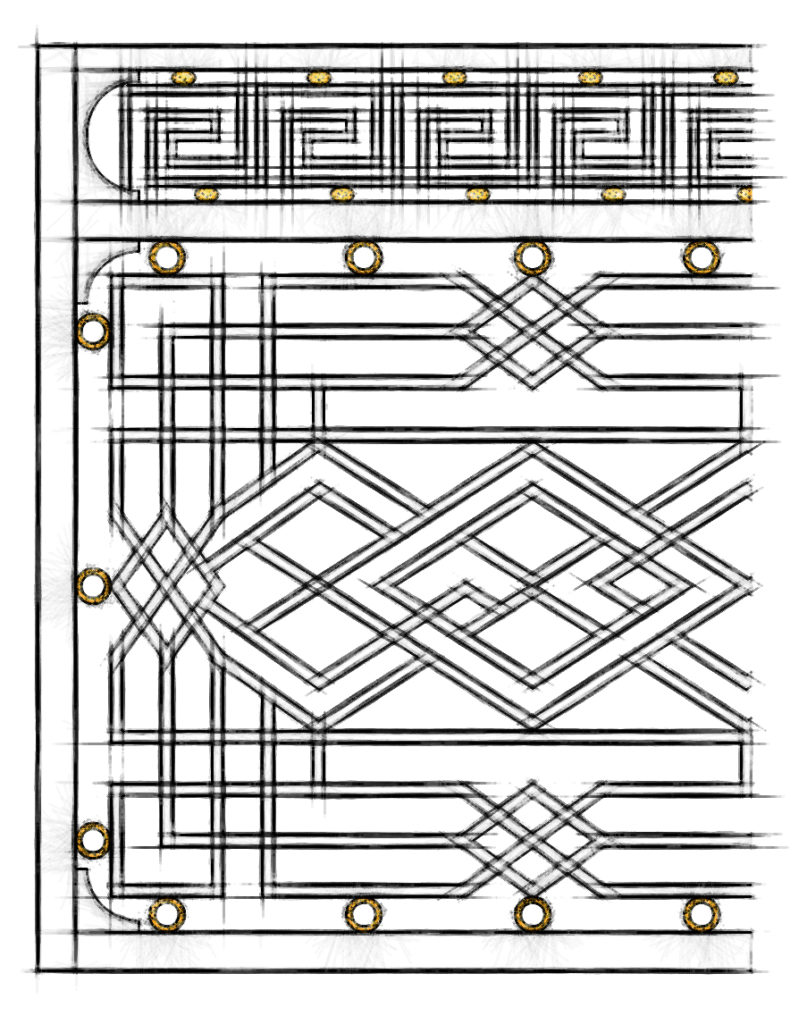
The style of architecture and design under King Louis 18 was a more eclectic development of French neoclassicism, incorporating elements of neo-Gothic and other styles. It was the first French decorative style imposed not by royalty, but by the tastes of the growing French upper class. In painting, neoclassicism and romanticism contended to became the dominant style.
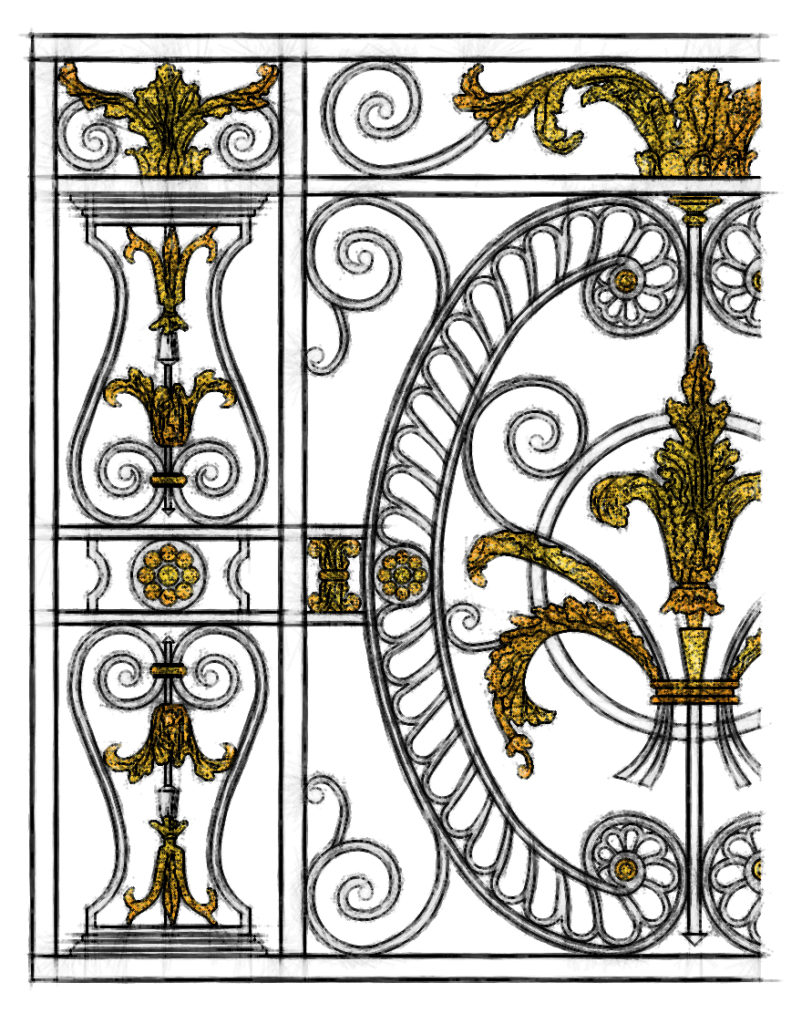

The Napoleon 3 style was a highly eclectic style of architecture and decorative arts, which used elements of many different historical styles and also made innovative use of modern materials, such as iron frameworks and glass skylights. It flourished during the reign of Emperor Napoleon 3 in France and had an important influence on architecture and decoration in the rest of Europe and the United States. The architectural style was closely connected with Haussmann’s renovation of Paris carried out during the Second Empire.
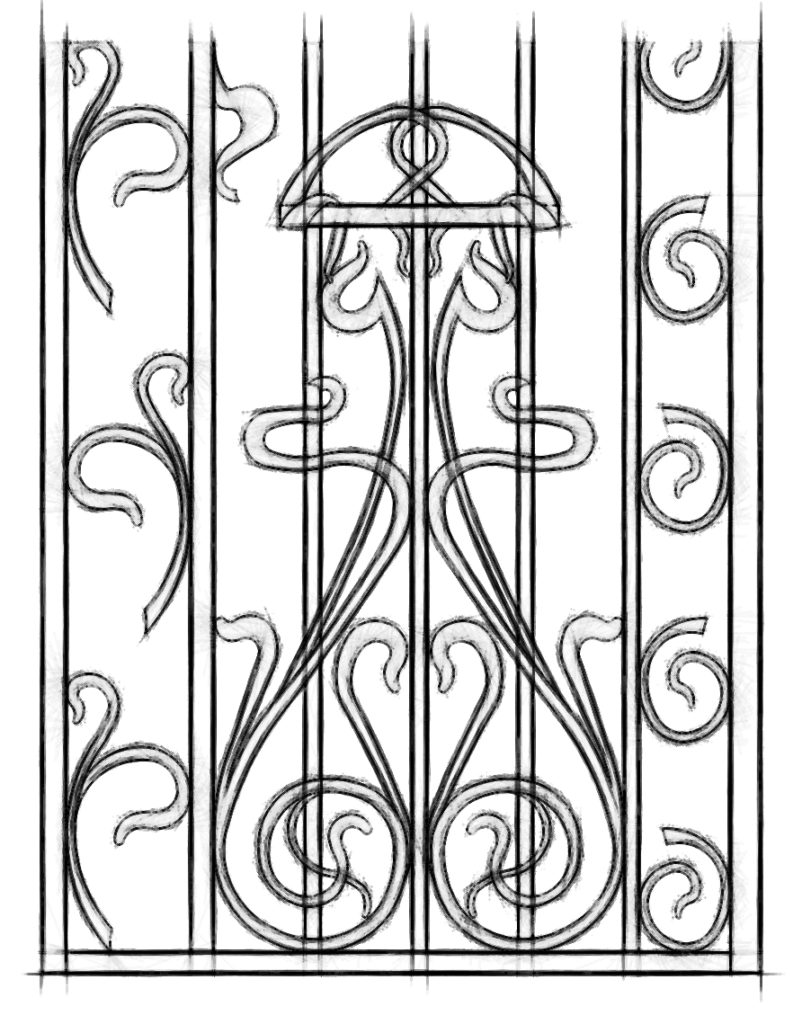
Art Nouveau is an international style of art, architecture and applied art, especially the decorative arts. It was most popular between 1890 and 1910. A reaction to the academic art of the 19th century, it was inspired by natural forms and structures, particularly the curved lines of plants and flowers.
Art Nouveau is a total art style: It embraces a wide range of fine and decorative arts, including architecture, painting, graphic art, interior design, jewelry, furniture, and metal work.
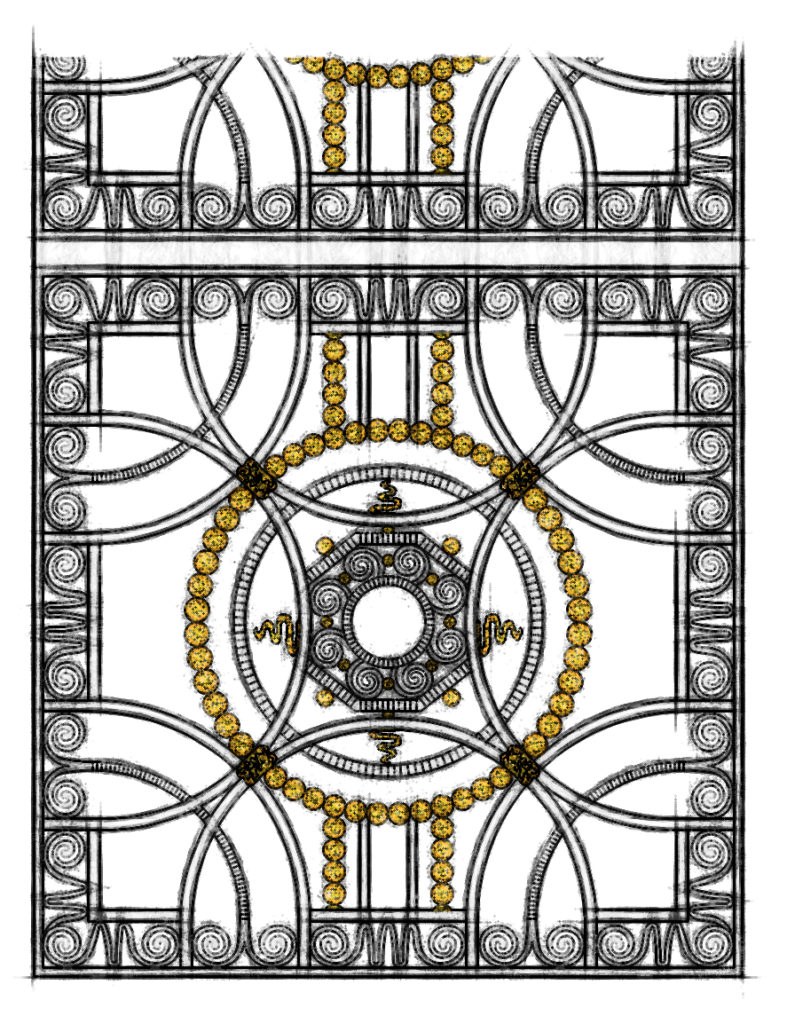
Art Deco, is a style of architecture and design that first appeared in France just before World War I. Art Deco influenced the design of buildings, furniture, jewelry, fashion, and everyday objects. It took its name, short for Arts Décoratifs, from the International Exhibition of Modern Decorative and Industrial Arts held in Paris in 1925. It combined modern styles with fine craftsmanship and rich materials. During its heyday, Art Deco represented luxury, glamour, exuberance, and faith in social and technological progress.
Art Contemporain is the art of today, produced in the second half of the 20th century or in the 21st century. Contemporary artists work in a globally influenced, culturally diverse, and technologically advancing world. Their art is a dynamic combination of materials, methods, concepts, and subjects that continue the challenging of boundaries that was already well underway in the 20th century. Diverse and eclectic, Art Contemporain as a whole is distinguished by the very lack of a uniform, organising principle, and ideology.
